What Are The Key Differences Between Hex Bolts and Hex Cap Screws?
Bolts and cap screws are both essential fasteners that are used in a wide range of applications. While they may seem similar, they have...

Bolts and cap screws are both essential fasteners that are used in a wide range of applications. While they may seem similar, they have some significant differences that can affect their performance and suitability for different tasks. In this blog, we will explore the key differences between bolts and cap screws to help you choose the right fastener for your needs.
Key Features of bolts and cap screwsBolts and cap screws differ in their design and features. One of the key differences is the presence of a bearing surface and chamfered end on the cap screw. The bearing surface, also known as the washer face, helps prevent damage to the mating surface during assembly. This is especially critical for assemblies using thin or soft materials. The chamfered end, also known as a point, reduces the potential for cross-threading with mating products. These features facilitate assembly and could help reduce the time and cost involved. It's important to note that only the hex cap screw has these features, making it an ideal choice for certain applications.
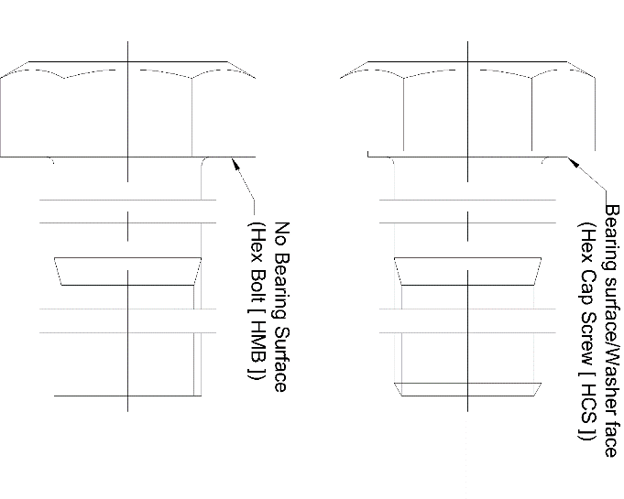
The under-head radii and body (or “shank”) diameters. The hex bolt; has a higher maximum tolerance on its under-head radius and body diameter than the cap screw which potentially makes its under-head juncture much sturdier and resistant to fracturing and failures. However, the lower side of its tolerances are below that of a typical cap screw. Which could provide varying results in performance.
Though similar, only the hex cap screw can be interchanged with most comparable assemblies using a hex bolt. Unfortunately, the same cannot be said for the hex bolt, as its larger tolerance zones could easily compromise the integrity of assemblies that primarily utilize hex cap screws.
When selecting a fastener, it is important to consider several factors, including the application, the materials being fastened, and the environmental conditions. It is important to choose the right fastener to ensure a secure and reliable connection.
The application in which the fastener will be used is another important consideration. For example, if the fastener will be used in a high-stress application, a cap screw may be preferred over a bolt. Similarly, if the fastener will be used in an application where it will be subject to vibration, to prevent the fastener from loosening, a hex bolt combined with a lock washer may be preferred over a hex cap screw with a thread-locking compound.
The application in which the fastener will be used is another important consideration when choosing the right fastener. For example, if the fastener will be used in a high-stress application, a cap screw may be preferred over a bolt. Similarly, if the fastener will be used in an application where it will be subject to vibration, a lock washer or thread-locking compound may be needed to prevent the fastener from loosening.
In conclusion, it's important to understand the key differences between bolts and cap screws, which primarily come down to their features and attributes. Hex cap screws have a bearing surface and chamfered end, while bolts do not. On the other hand, bolts have a higher maximum tolerance on their under-head radii and body diameter, which potentially makes their under-head juncture much sturdier than cap screws. However, cap screws are more interchangeable with other assemblies. When choosing the right fastener for your needs, it's important to consider the application and materials being used. By following these guidelines and understanding the differences between bolts and cap screws, you can make informed decisions and ensure the integrity of your assemblies.
Bolts and cap screws are both essential fasteners that are used in a wide range of applications. While they may seem similar, they have...
Coupling nuts are useful tools that often don't get enough attention—especially hex coupling nuts. They can help complete many different...
Coupling nuts are useful tools that often don't get enough attention—especially hex coupling nuts. They can help complete many different...
